By Atul Kurani
The global healthcare sector has witnessed massive transformation in the recent years. Numerous technological innovations, across the physical and digital landscapes, have accelerated the said revolution and some of them possess great business potential too. Innovations in extended reality (XR) and its forms of immersive technologies—augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR)—have steered the healthcare sector toward new opportunities and solutions.
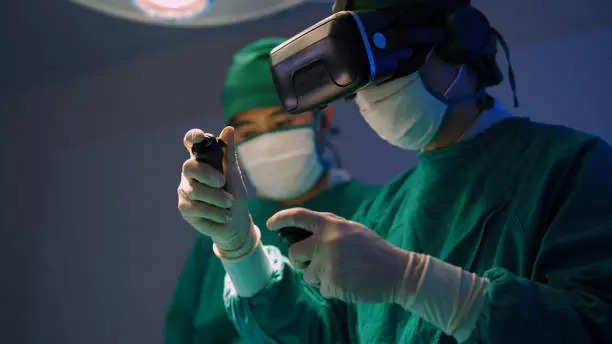
AR/VR are being leveraged to deliver more convenient, modern, streamlined, and effective healthcare services to patients. These immersive technologies are also assisting surgeons, doctors and nurses in diagnosis, treatment, surgery, training, and long-term condition management. From using AR/VR tools for enhanced training and procedure planning to enabling remote surgery with tele-robotics integrated into an AR-enabled telesurgery platform, digital surgery solutions have come a long way. This, along with the implementation of haptic technology for sense of touch/feel of tissues, is expected to revolutionise surgical procedures. AR/VR solutions could significantly add value to telerehabilitation programs for remote post-surgical care, minimising hospital visits and improving outcomes.
Innovation to impact
When one thinks of XR and its various aspects, the Metaverse sure comes into the picture. XR-related innovation could easily create bigger opportunities within the Metaverse such as remote collaboration, sharing of global medical standards and best practices, higher peer-to-peer engagement, and initiatives that could usher in the next wave of discoveries. The number of existing use cases reiterates the many benefits of XR for the healthcare industry.
VR systems including important elements of neurobiology and motor learning have been developed to aid stroke patients in their motor rehabilitation. A solution named XRHealth offers VR/AR therapy in the Metaverse to those ailing from Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). It helps connect with therapists and get autism-related disorders treated from homes. These technologies not only address prevailing health conditions but also enable inclusion. For instance, a Japanese café, DAWN10 (Diverse Avatar Working Network) hires human pilots with impairments to operate robots, providing accessible hospitality jobs to those who are frequently bedridden and unable to leave their homes.
The pandemic also favoured the advancement of connected tools used for immersive training. With a combination of AR/VR technologies in the Metaverse, the healthcare industry can augment the quality of medical trainings and increase the number of professionals. This would also culminate in improved care, precision, and reduce the cost of purchasing equipment.
The evolution of healthcare
It goes without saying that evolution is fundamental to growth. The healthcare sector too has evolved, with developers and innovators working on integrating new-age technologies such as cloud computing, virtual and extended realities, sensors, and 5G into care delivery models. The industry is also embracing more advanced technologies of quantum computing and the Metaverse to deepen its reach and sharpen its ability in the life sciences and healthcare space. The convergence of connected devices and applications is slowly but steadily giving rise to the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT).
The usage of data and analytics is another component of value to the healthcare industry. The data generated from people’s daily lives can often be relevant for medical outcomes. Thus, it is necessary that innovations are made to build new analytical tools converting raw data into actionable insights.
Acknowledging the hurdles
Healthcare industries across the world are usually restricted in their approach, and rightly so, as people’s health and lives are at stake. They also have several regulations in place, which could make testing of XR and related technologies in the Metaverse difficult. To start with, these technologies must ensure a rock-solid structural and legal foundation for regulatory bodies to allow their deployment at scale. Treatment and surgery in virtual worlds through AR/VR would require gaining trust for widespread adoption of these technologies by the healthcare sector. Insurance and reimbursements against medical treatment via XR could also face challenges. Major insurance companies and the healthcare industry will need to work out the details of such claims.
Governments, policymakers, entrepreneurs, industry experts, and healthcare professionals must form enabling ecosystems with secure and trustworthy virtual infrastructure while providing attractive incentives to encourage innovation and wider adoption of XR. As the demand for efficient and economical healthcare and wellbeing services rises, XR and related technologies can greatly complement the physical industry by enhancing accessibility and delivering care in real time.
Atul Kurani, VP, Global Health Medical Practice & IoT, Capgemini Engineering, India
(DISCLAIMER: The views expressed are sole of the author and ETHealthworld does not necessarily subscribe to it. ETHealthworld.com shall not be responsible for any damage caused to any person/organisation directly or indirectly)
Credit: Source link